Step down transformers are crucial electrical devices that play a vital role in reducing voltage levels. They find widespread applications in various industries and settings where lower voltages are required. By stepping down the voltage, these transformers enable the safe and efficient operation of electrical equipment, providing compatibility with devices that operate on lower voltage levels. Read More…
With more than 500 current transformer manufacturers in the world, Triad Magnetics realizes you have a choice. Why choose Triad? Having served the needs of many industries for more than half a century, Triad believes its experience makes the difference. And if there is one point experience has taught it, it is that it must remain flexible and adaptable to the changing needs of the market.
Lenco Electronics, Inc. specializes in a wide variety of custom electric transformers. Lenco’s success has not come about by accident, but by providing its customers with high-quality products.

Bicron Electronics specializes in high efficiency toroidal transformers up to 10KVA with safety recognitions from UL, CSA, VDE, TUV and IEC as well as high frequency transformers up to 10MHz for isolation, gate drive, pulse and switch mode functions. Bicron is ISO 9001:2000 certified.

We design and manufacture Toroidal Transformers, Inductors and Current Transformers in Connecticut, USA and Asia. Certified to UL/CSA/IEC/EN. CE marking. Applications from lighting to medical devices. Customers served Worldwide. For High Frequency Magnetics, visit our affiliate www.Induktorusa.com

ISO 9001:2000 registered Sun Transformer creates custom transformers optimized for the needs of many industries. Large power, isolation & auto transformers, printed circuit mount power transformers, units for hostile conditions, units with ferrite or nickel cores for digital telecommunications use, etc.

More Step Down Transformer Manufacturers
Differences from Other Transformers
Step down transformers differ from other types of transformers in terms of their specific applications. While step up transformers are designed to increase voltage levels, step down transformers are utilized for voltage reduction. Power transformers, which are commonly used in power transmission and distribution, are distinct from step down transformers as they are designed to handle significantly higher power levels.
Components of Step Down Transformers
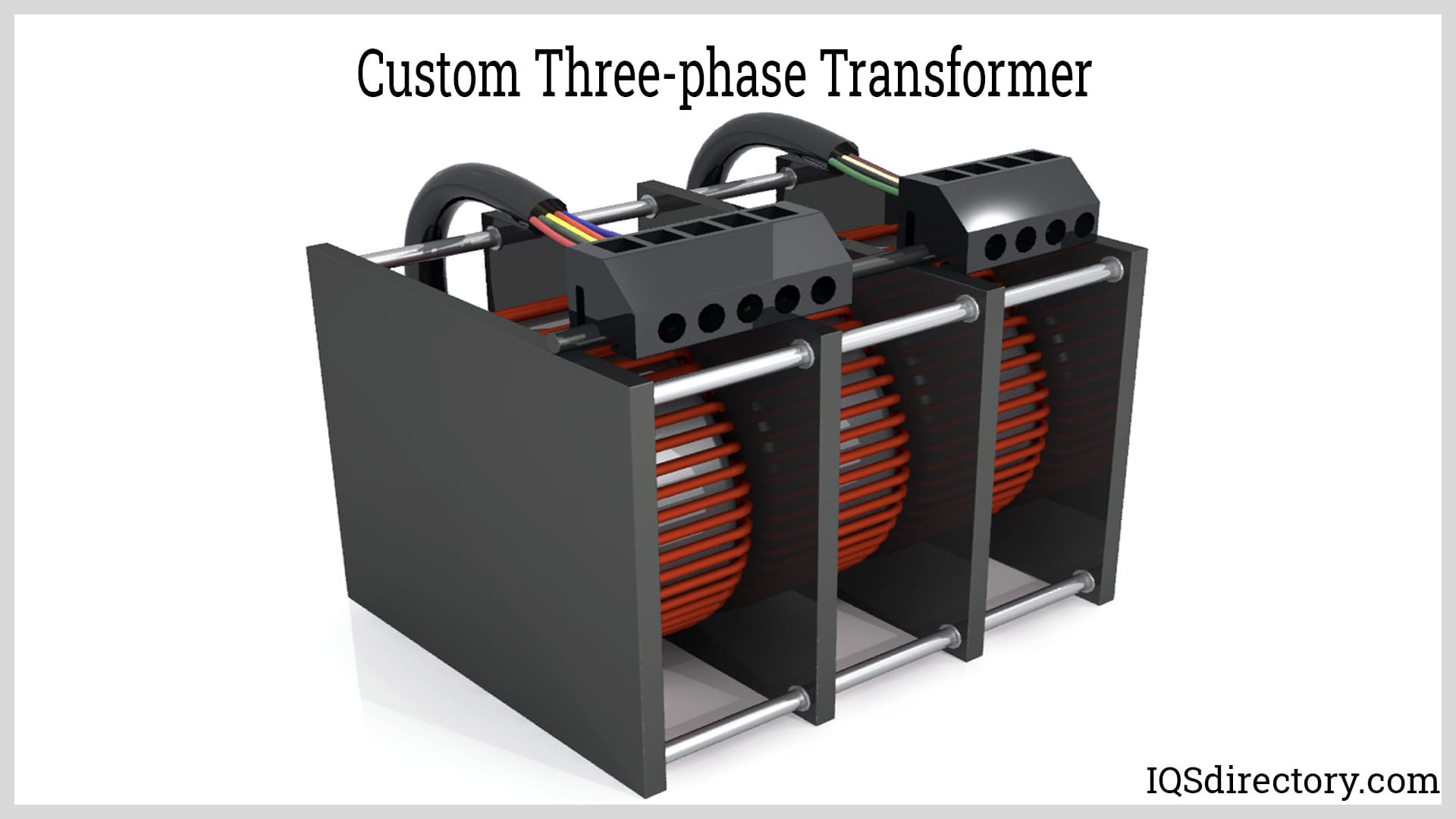
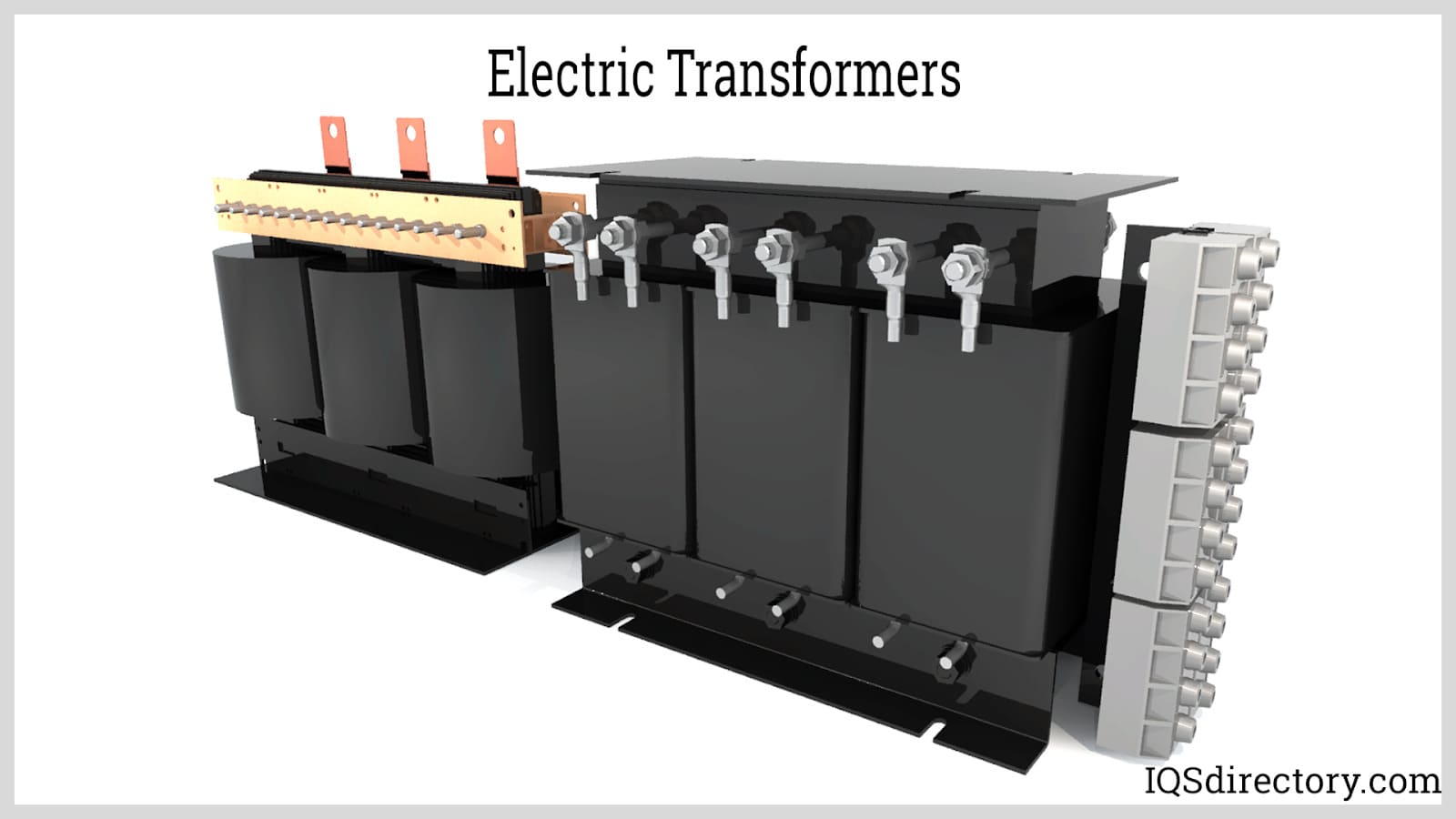
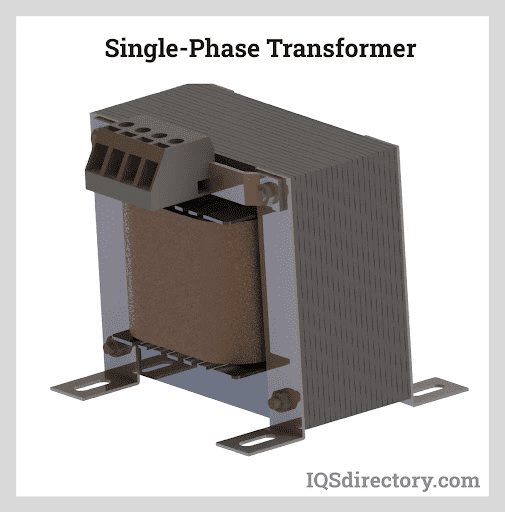
Every step down transformer comprises several essential components that work together to facilitate voltage reduction. The primary winding serves as the input for the transformer, receiving the higher voltage from the power source. The secondary winding, on the other hand, delivers the stepped-down voltage to the load. Both windings are typically made of insulated copper wire to ensure electrical conductivity while maintaining isolation. The magnetic core, typically constructed of laminated steel or ferrite material, enhances magnetic induction and facilitates efficient energy transfer. Additionally, insulation and cooling systems are incorporated into the transformer design to ensure safe operation and prevent overheating.
Varieties of Step Down Transformers
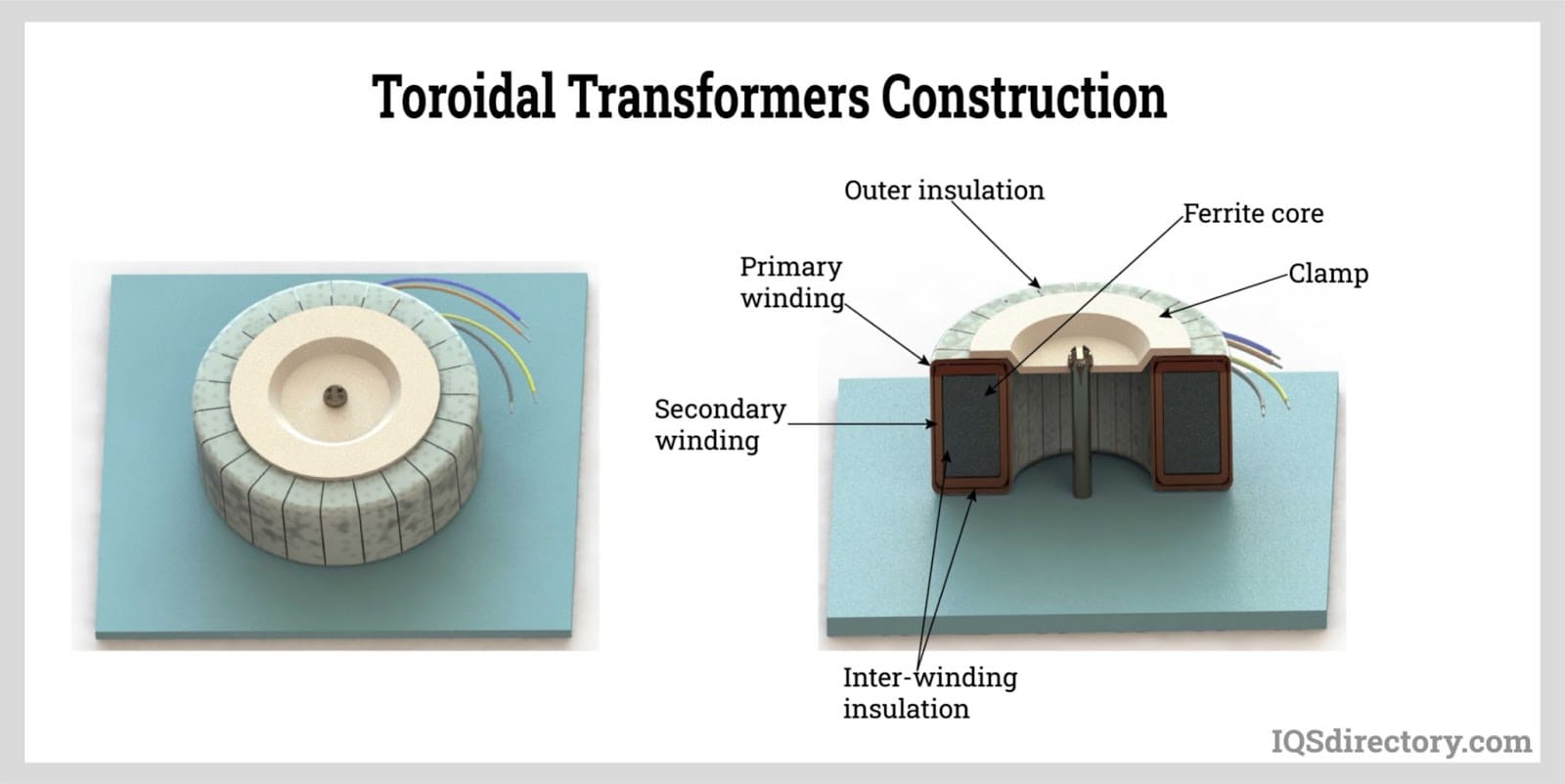
Step down transformers come in various forms, each designed to cater to specific applications. One such variety is the toroidal step down transformer, which features a toroidal-shaped core. These transformers are commonly used in audio systems, where they provide voltage reduction without compromising the audio quality. Autotransformers are another type that is often employed for voltage regulation in electrical systems. They are capable of stabilizing voltage fluctuations and ensuring consistent output voltage levels. Isolation transformers, on the other hand, are frequently found in medical equipment, offering electrical isolation and enhancing safety for both patients and medical professionals.
Considerations of Step Down Transformers
Despite their many benefits, step down transformers have a few considerations to be aware of. One issue is energy losses and inefficiency, as a portion of the input energy is lost during the transformation process. Another concern is potential electromagnetic interference (EMI) caused by the magnetic fields generated by the transformer. Additionally, voltage drops and regulation issues may occur if the transformer is not properly designed or if the load fluctuates significantly.
Manufacturers Address These Considerations
Manufacturers of step down transformers have taken several steps to mitigate these considerations. Improved design techniques and the use of high-quality materials have contributed to increased efficiency and reduced energy losses. Additionally, shielding and filtering techniques have been implemented to minimize electromagnetic interference, ensuring the transformer's operation does not interfere with other sensitive electronic equipment. Advanced voltage regulation methods, such as feedback control systems, have also been employed to enhance voltage stability and minimize regulation issues.
Benefits of Step Down Transformers
Step down transformers offer a range of benefits that make them indispensable in various applications. One significant advantage is electrical safety and isolation. By reducing voltage levels, they provide a safer operating environment, particularly for low-voltage devices and sensitive equipment. This helps protect both users and the connected devices from potential electrical hazards. Additionally, step down transformers ensure compatibility with lower voltage devices, allowing seamless integration into existing electrical systems. They bridge the gap between different voltage requirements, enabling the use of devices that operate on lower voltage levels. This versatility enhances flexibility and convenience in power distribution. Moreover, step down transformers provide voltage conversion capabilities, allowing the efficient adaptation of electrical systems to varying voltage requirements. This is particularly useful in international settings where different countries may have different voltage standards. Overall, step down transformers contribute to the efficient and reliable operation of electrical systems, ensuring the proper functioning of devices while prioritizing safety and compatibility.
Applications of Step Down Transformers
Various industries rely on step down transformers for their specific applications. In residential and commercial settings, step down transformers power essential household appliances such as refrigerators, air conditioners, lighting systems, and audio equipment. In the realm of audio systems, toroidal step down transformers are particularly valuable. They ensure a smooth and efficient reduction in voltage levels without compromising the audio quality, making them ideal for powering amplifiers, mixers, and speakers. Another critical domain where step down transformers find extensive use is in the medical field. Isolation transformers play a vital role in medical equipment, providing electrical isolation and enhancing patient safety. They help prevent electrical shocks and ensure that medical devices operate reliably and safely, making them indispensable components in hospitals, clinics, and diagnostic centers. Additionally, step down transformers are prevalent in electronics and telecommunications industries, powering various electronic devices and facilitating voltage conversion for international communication.
Choosing the Right Step Down Transformer Supplier
To ensure you have the most productive outcome when purchasing step down transformers from a step down transformer supplier, it is important to compare several companies using our directory of step down transformer suppliers. Each step down transformer supplier has a business profile page highlighting their areas of experience and capabilities, along with a contact form to directly communicate with the supplier for more information or to request a quote. Review each step down transformer business website using our patented website previewer to quickly learn what each company specializes in. Then, use our simple RFQ form to contact multiple step down transformer companies with the same form.










 Electric Coils
Electric Coils Electric Switches
Electric Switches Electric Transformers
Electric Transformers Electronic Connectors
Electronic Connectors Electronic Enclosures
Electronic Enclosures EMI Shielding
EMI Shielding Membrane Switches
Membrane Switches Power Cords
Power Cords Static Eliminators
Static Eliminators Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services