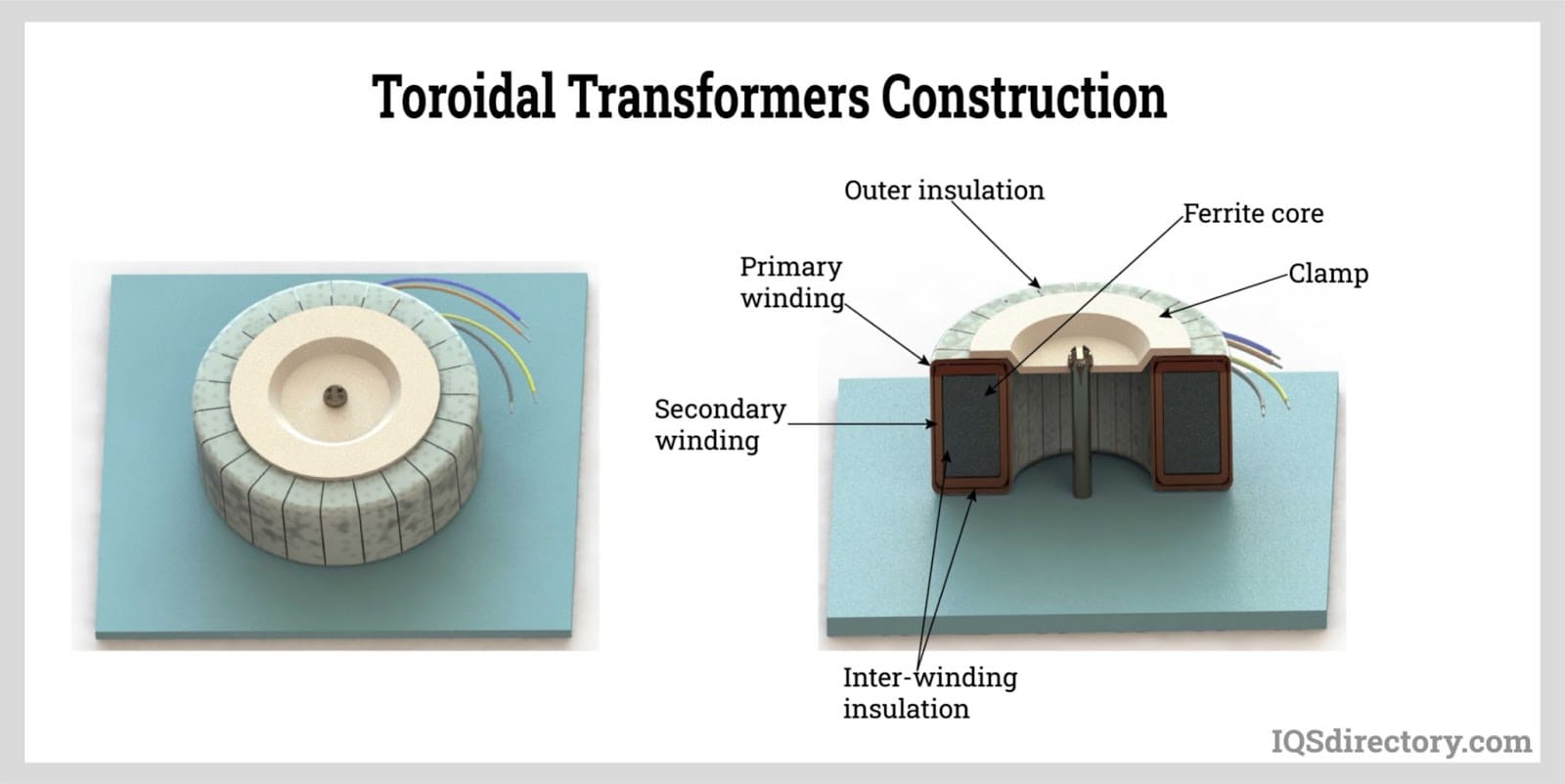
A toroidal transformer is an electrical transformer with a torus or donut-shaped core. The torus core’s surface is covered by its primary and secondary windings, spaced apart by an insulating substance. Any magnetic flux leakage is minimized in this design. Toroidal transformers provide several advantages over conventional square and rectangular-shaped transformers, making them appropriate for delicate and important electronic circuits. Read More…
With more than 500 current transformer manufacturers in the world, Triad Magnetics realizes you have a choice. Why choose Triad? Having served the needs of many industries for more than half a century, Triad believes its experience makes the difference. And if there is one point experience has taught it, it is that it must remain flexible and adaptable to the changing needs of the market.
Lenco Electronics, Inc. specializes in a wide variety of custom electric transformers. Lenco’s success has not come about by accident, but by providing its customers with high-quality products.

Bicron Electronics specializes in high efficiency toroidal transformers up to 10KVA with safety recognitions from UL, CSA, VDE, TUV and IEC as well as high frequency transformers up to 10MHz for isolation, gate drive, pulse and switch mode functions. Bicron is ISO 9001:2000 certified.

We design and manufacture Toroidal Transformers, Inductors and Current Transformers in Connecticut, USA and Asia. Certified to UL/CSA/IEC/EN. CE marking. Applications from lighting to medical devices. Customers served Worldwide. For High Frequency Magnetics, visit our affiliate www.Induktorusa.com

ISO 9001:2000 registered Sun Transformer creates custom transformers optimized for the needs of many industries. Large power, isolation & auto transformers, printed circuit mount power transformers, units for hostile conditions, units with ferrite or nickel cores for digital telecommunications use, etc.

More Toroidal Transformer Manufacturers
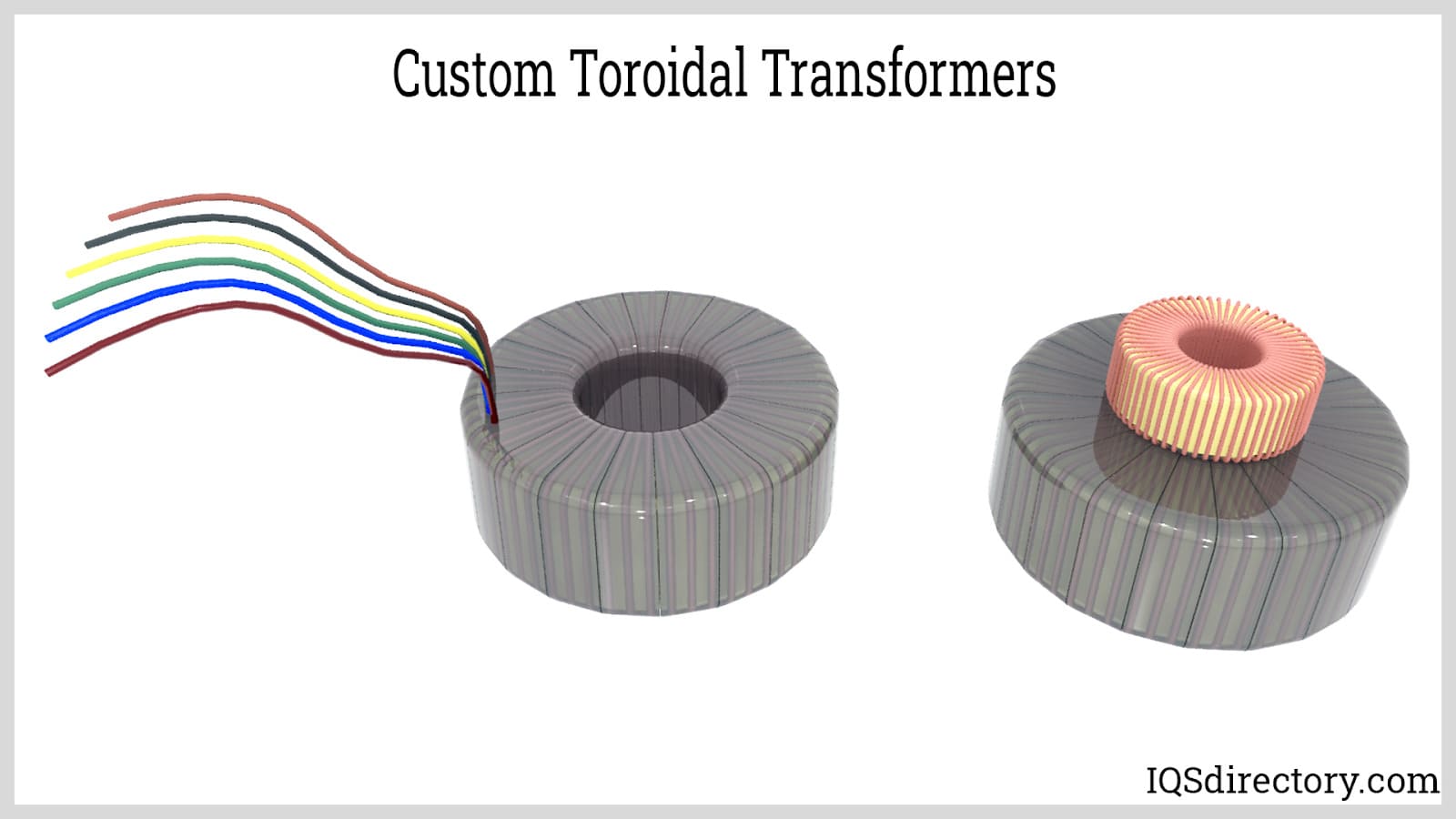
Compared to conventional shell and core-type transformers, toroidal transformers offer greater design freedom, efficiency, and compactness. They are the perfect solution for low-KVA of up to 15 KVA-rated devices and machinery used in industrial, medical, audio applications, and renewable energy.
Toroidal Transformer Operating Principle
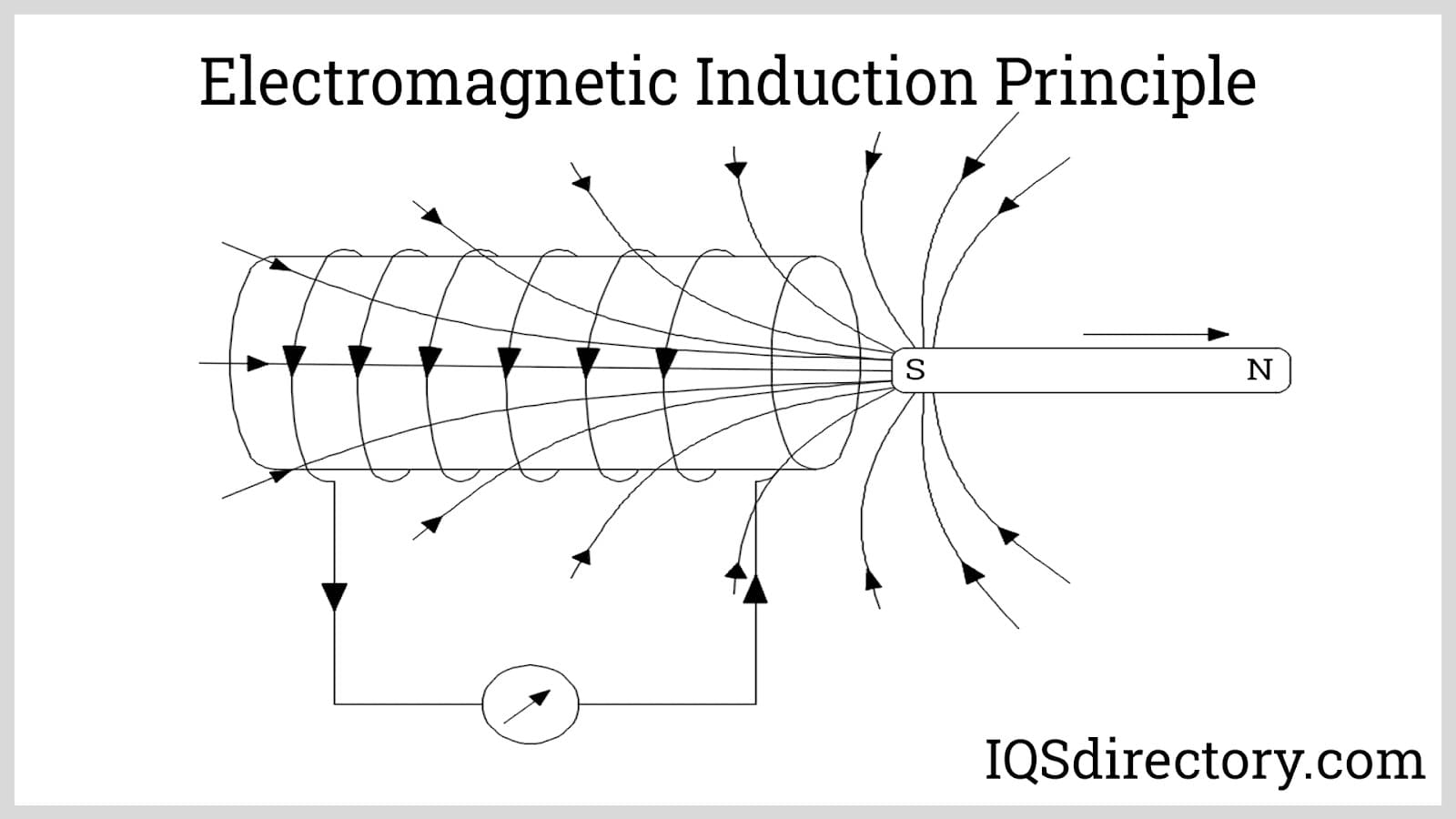
A passive electrical transformer uses a magnetic field to create an electromotive force to move electricity from one circuit to another. The circuits are electrically segregated from one another while this is being done. Transformers are used to change the voltage without altering the frequency of the current flow as it steps up or down the voltage. Faraday's law of induction is the basis for how electrical transformers function.
This physical equation describes the connection between the induced electromotive force and the rate at which a magnetic flux changes. A magnetic flux is produced when magnetic field lines go through a conductor. It was discovered that placing a conductor close to a magnetic field with variable amplitude causes that conductor to produce an electric current.
Solenoids and toroids are the two types of transformer core forms. In order to be considered a solenoid, the conductor must be long and thin and coil up into numerous, close-knit loops. A perfect toroid would completely contain the magnetic flux, similar to a perfect solenoid. In contrast to the absence of magnetic flux density outside the coil, it is concentrated inside.
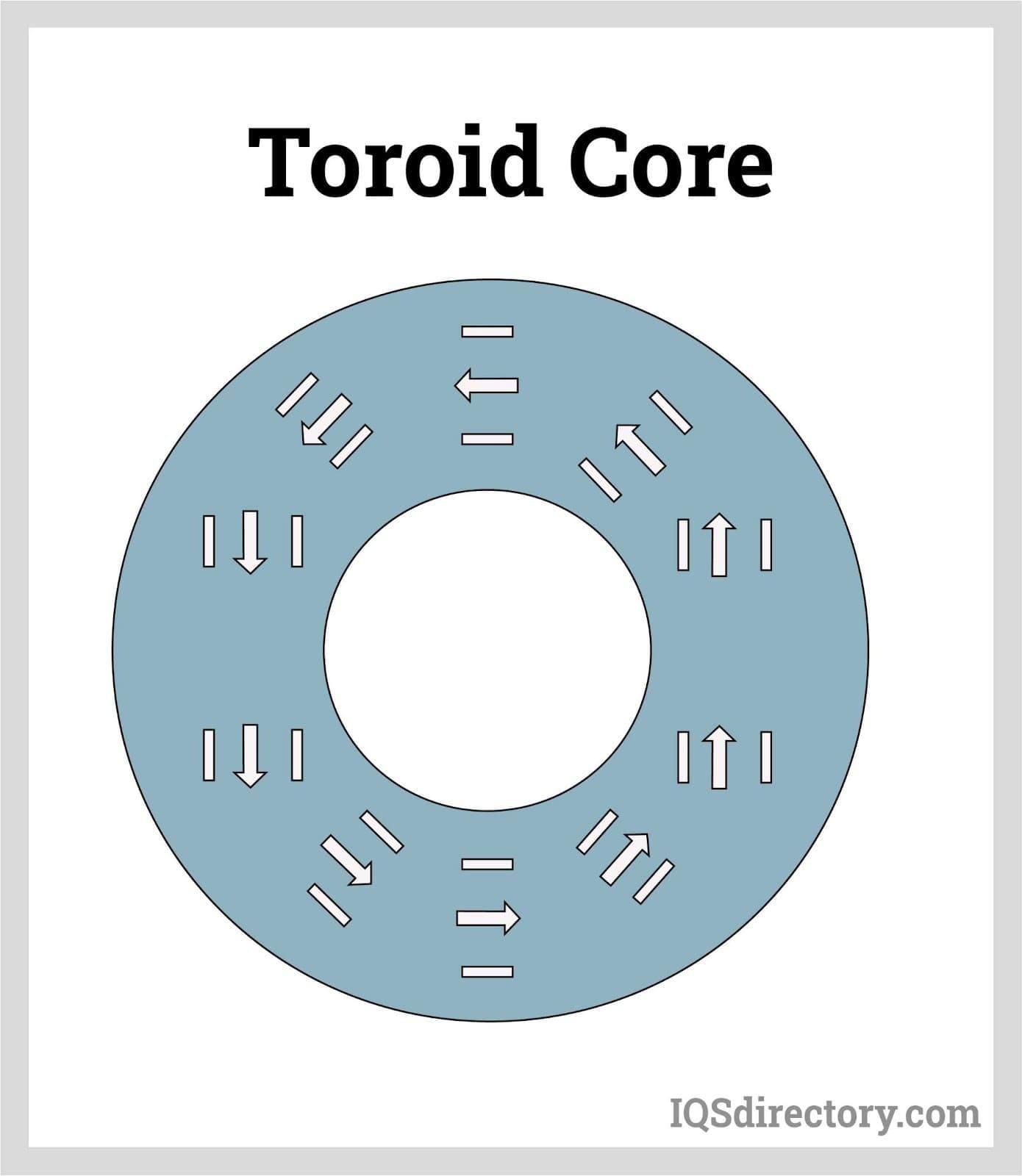
A toroid core's optimal design is significantly more attainable than a solenoid's. Since it is set up as a loop, it does not have to be indefinitely long. The only prerequisite for a flawless design is to wind the toroid as a whole with windings that are uniformly and tightly coiled. This is probably why Faraday employed a toroidal core rather than a solenoid when he discovered induction. A toroid's circular design makes it simple for the magnetic flux to form a loop without needing an additional return path.
Advantages of Toroidal Transformers
High Efficiency
With typically between 95 and 99% efficiency, toroidal transformers are more efficient than other transformers. This is due to the design's near-optimal construction, which perfectly seals the magnetic flux within the windings. As a result, there is no flux leakage. The magnetic flux is effectively used to couple the main and secondary windings because it is concentrated inside the coil windings, and the windings are uniformly distributed throughout the toroid core.
Electromagnetic Shielding
Toroidal cores naturally insulate nearby components against electromagnetic interference due to the efficient magnetic flux (EMI) containment. They are ideal for electronic devices with delicate components because of this property.
Lower Off-load Losses
Off-load losses occur when the transformer's core is magnetized even though no load is attached to the secondary circuit. As a result, transformers frequently use energy even when they are on standby. Due to their efficient construction, core losses in toroidal transformers are smaller than in regular solenoid-core transformers. Toroidal has fewer off-load losses as a result.
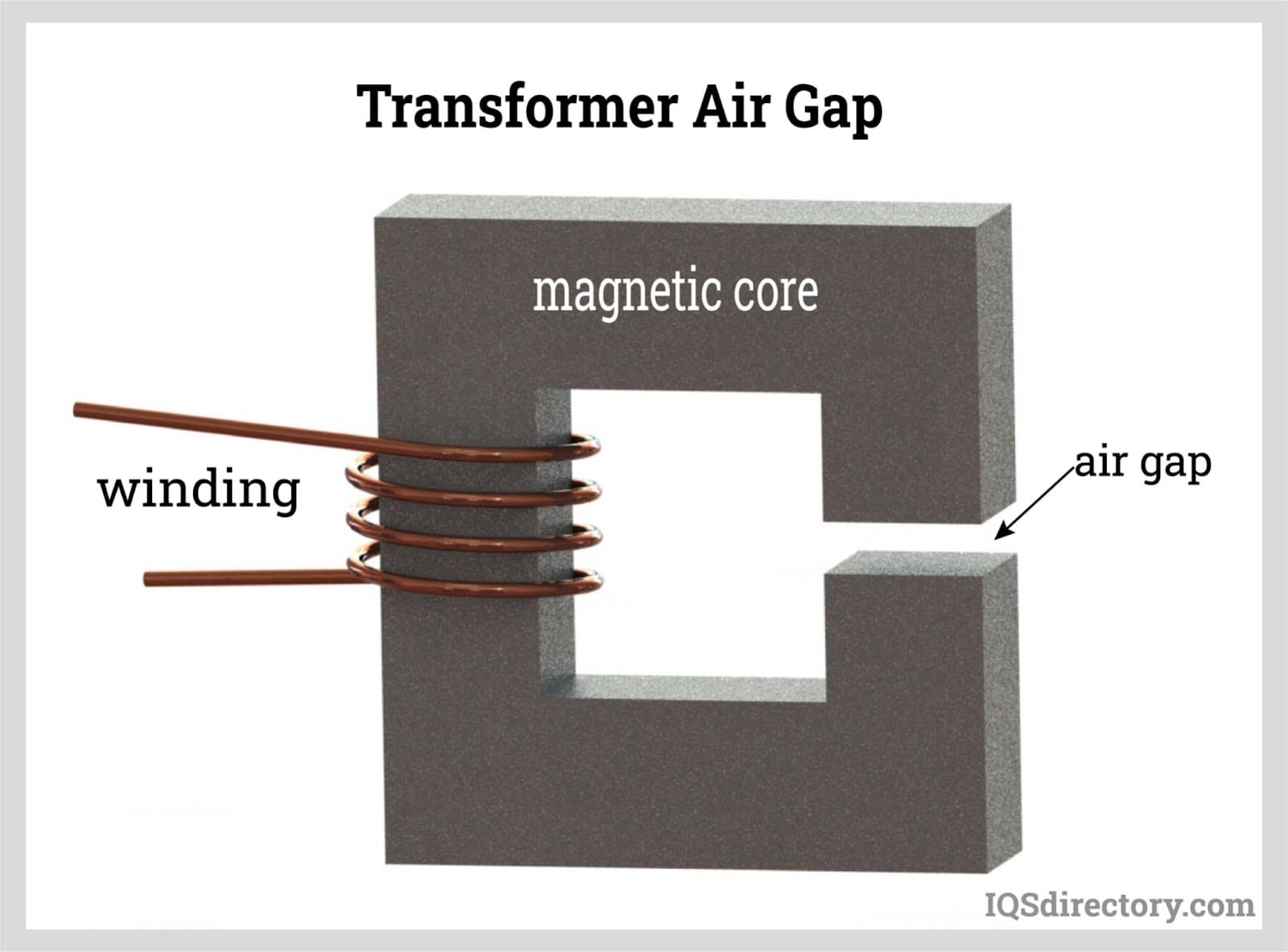
No Air Gap
In contrast to solenoid cores, which have a continuous structure with a significant air gap, toroidal cores are built differently. Air gaps contribute to various detrimental impacts, including noise and the propagation of magnetic flux, or fringing. Three air gaps are present in a typical solenoid core, such as an EI core. Magnetic flux leaks travel via nearby exterior parts at these sites.
Lower Heat Generation
Transformer electrical energy losses eventually result in vibrations and heat. Hysteresis, copper resistance, and eddy currents are the main sources of heat generation. Due to their great efficiency, toroidal transformers produce less heat and can operate without coolant or heat sinks.
Disadvantages of Toroidal Transformers
Expensive Construction
Toroidal transformers are more expensive to produce than other types of transformers, having lower profiles and requiring fewer materials.
Higher Inrush Currents
When the transformer is switched on, there is a surge in the current known as inrush current. This is caused by the primary circuit using a lot of initial currents when the secondary circuit is coupled to a load. In highly efficient transformers like toroid transformers, the amount of inrush current is larger.
Suitable For Single Phase Application
The use of toroidal transformers is restricted to single-phase systems. Three-phase toroidal transformers are marketed but are less common than the more traditional core and shell-type transformers. Only specific applications require the usage of three-phase toroidal transformers.
Application of Toroidal Transformers
- Power supply systems
- Power inverters
- Audio systems
- Control equipment
- Other electronic devices
Choosing the Correct Toroidal Transformer Supplier
For the most productive outcome when purchasing toroidal transformers from a toroidal transformer supplier, it is important to compare several suppliers using our directory of toroidal transformer companies. Each toroidal transformer supplier has a business profile page highlighting their areas of experience and capabilities, and a contact form to directly communicate with the supplier for more information or request a quote. Review each toroidal transformer business website using our patented website previewer to get an idea of what each company specializes in. Then, use our simple RFQ form to contact multiple toroidal transformer businesses with the same form.










 Electric Coils
Electric Coils Electric Switches
Electric Switches Electric Transformers
Electric Transformers Electronic Connectors
Electronic Connectors Electronic Enclosures
Electronic Enclosures EMI Shielding
EMI Shielding Membrane Switches
Membrane Switches Power Cords
Power Cords Static Eliminators
Static Eliminators Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services